Municipalities have the burden of managing aging critical infrastructure while also attempting to future-proof against unprecedented risks, whether from climate change or human action.
By diving deep into scenarios, investments and human impact calculations, we’re helping municipalities activate resilience for their critical services and resources.
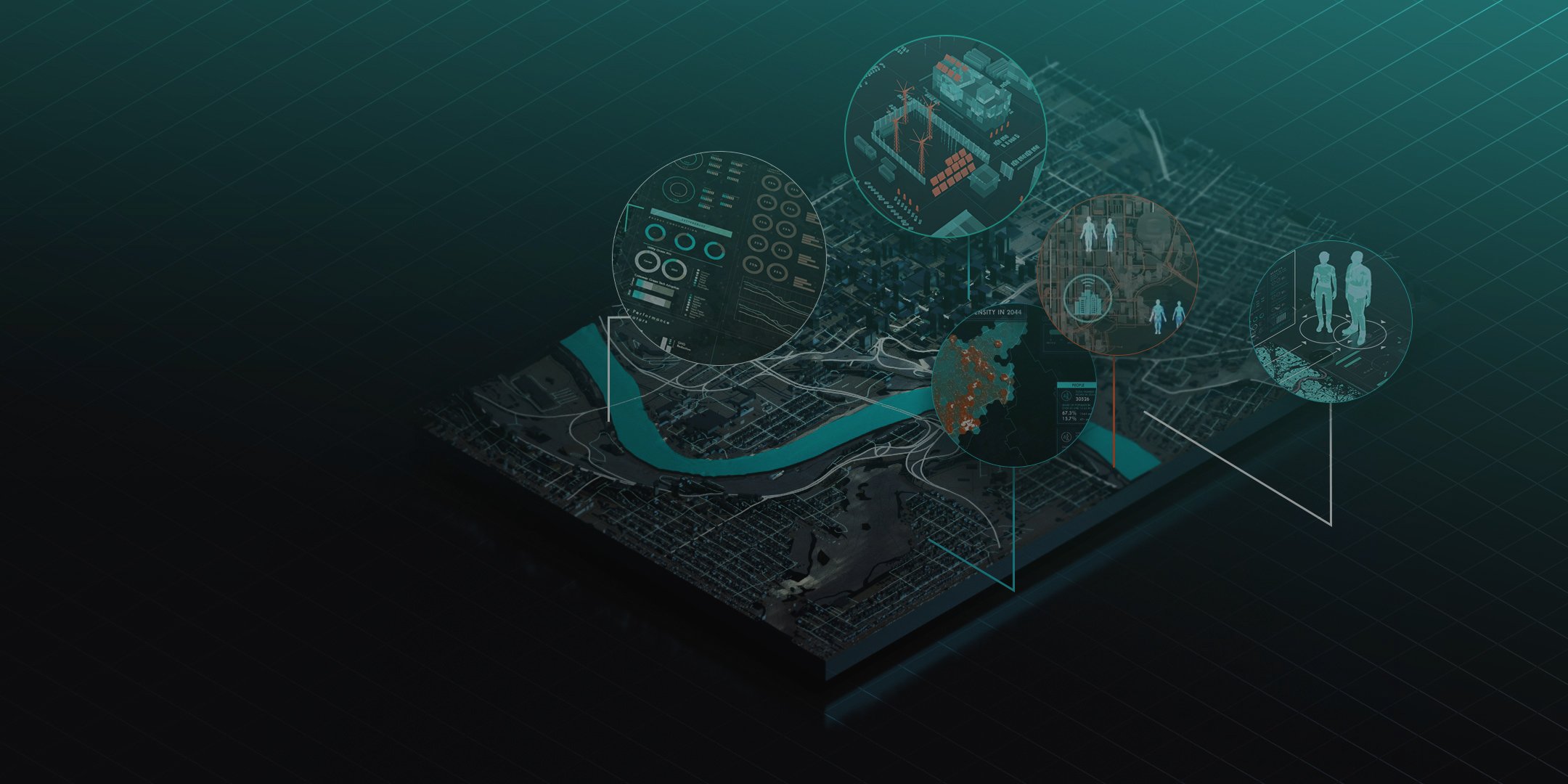
RWI creates a live, interconnected Synthetic Twin fusing engineering data, spatial context, and synthetic populations to reveal how disruptions ripple through networks and communities.
These twins advance fragmented data to strategic planning, providing a sandbox where virtual scenarios replace best guesswork, resulting in faster vulnerability assessment, reduction in downtime risk, and better capital gain through optimized investments.
Less guesswork means better resilience and significant cost savings.
When it comes to securing infrastructure, keeping populations safe, and managing budgets, Synthetic Twins forecast unprecedented tomorrows, today.
Connected Intelligence
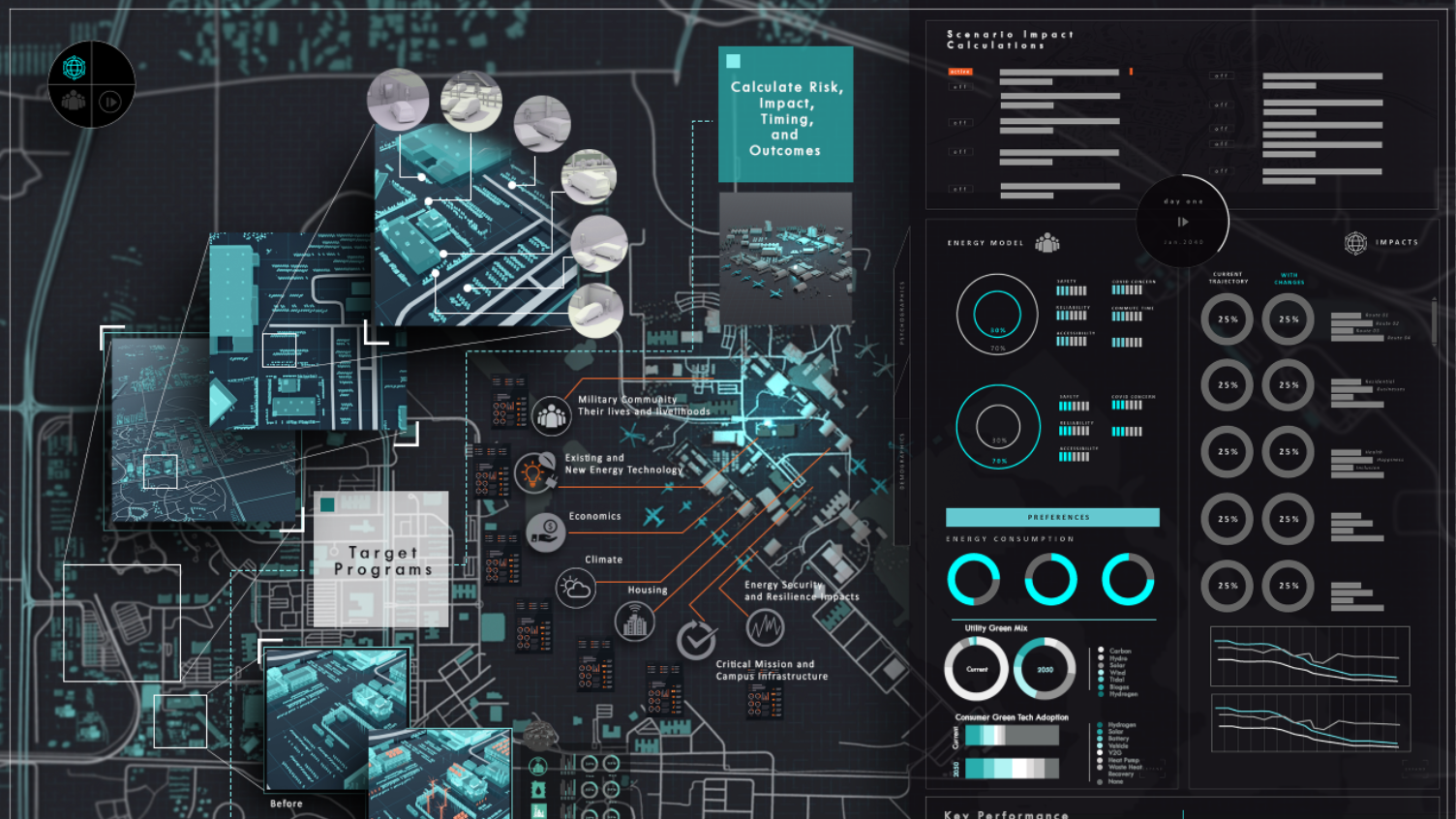
RWI’s “systems-seeing” platforms allow the future of energy to become inflectable, configurable, interactive, and visualized.
Active Intelligence
Measuring Water Efficiency in California
Water efficiency is critical for thriving cities, supporting populations and industries while mitigating climate change and drought impacts, especially in regions like Southern California. We modeled residential water use by rethinking how usage behaviors are measured and integrating age, demographics, population, and time-of-day data.
Simulating Extreme Cold in Nashville
In a pilot with the Tennessee Valley Authority, we simulated an extreme cold snap and power outage in Nashville to show grid impacts and community vulnerabilities, particularly in lower-income neighborhoods.
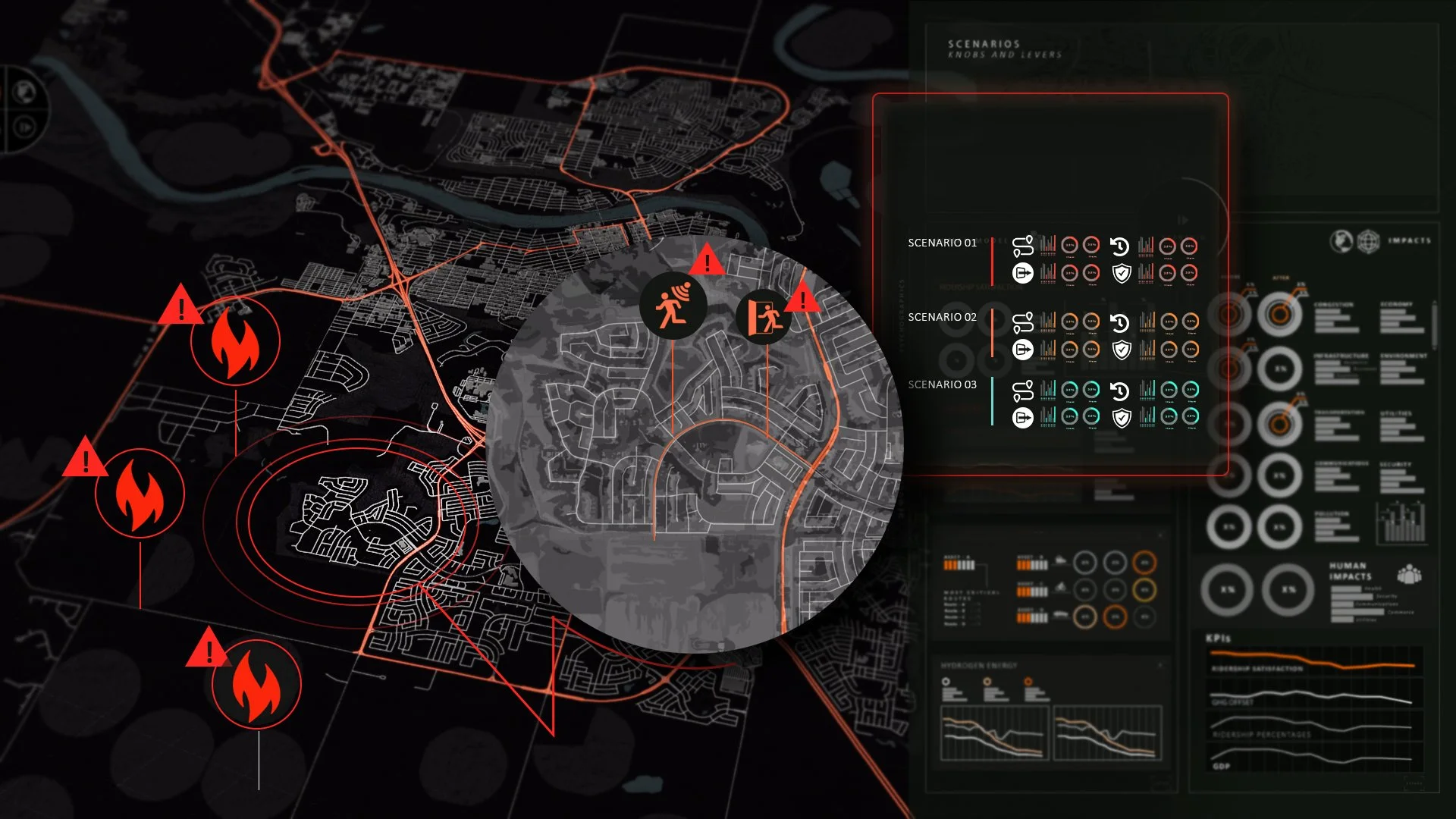
Synthesizing Wildfire Evacuations
In Western Canada, rising urban-wildfire interactions prompt emergency responders to identify infrastructure and policy risks, and RWI’s Synthetic Intelligence helps municipalities find the most efficient, cost-effective, and human-focused evacuation options.
Modelling Energy Security
RWI is testing a web-based 6D shared interface that lets users interactively model energy security and resilience by adjusting variables across climate and human impacts.
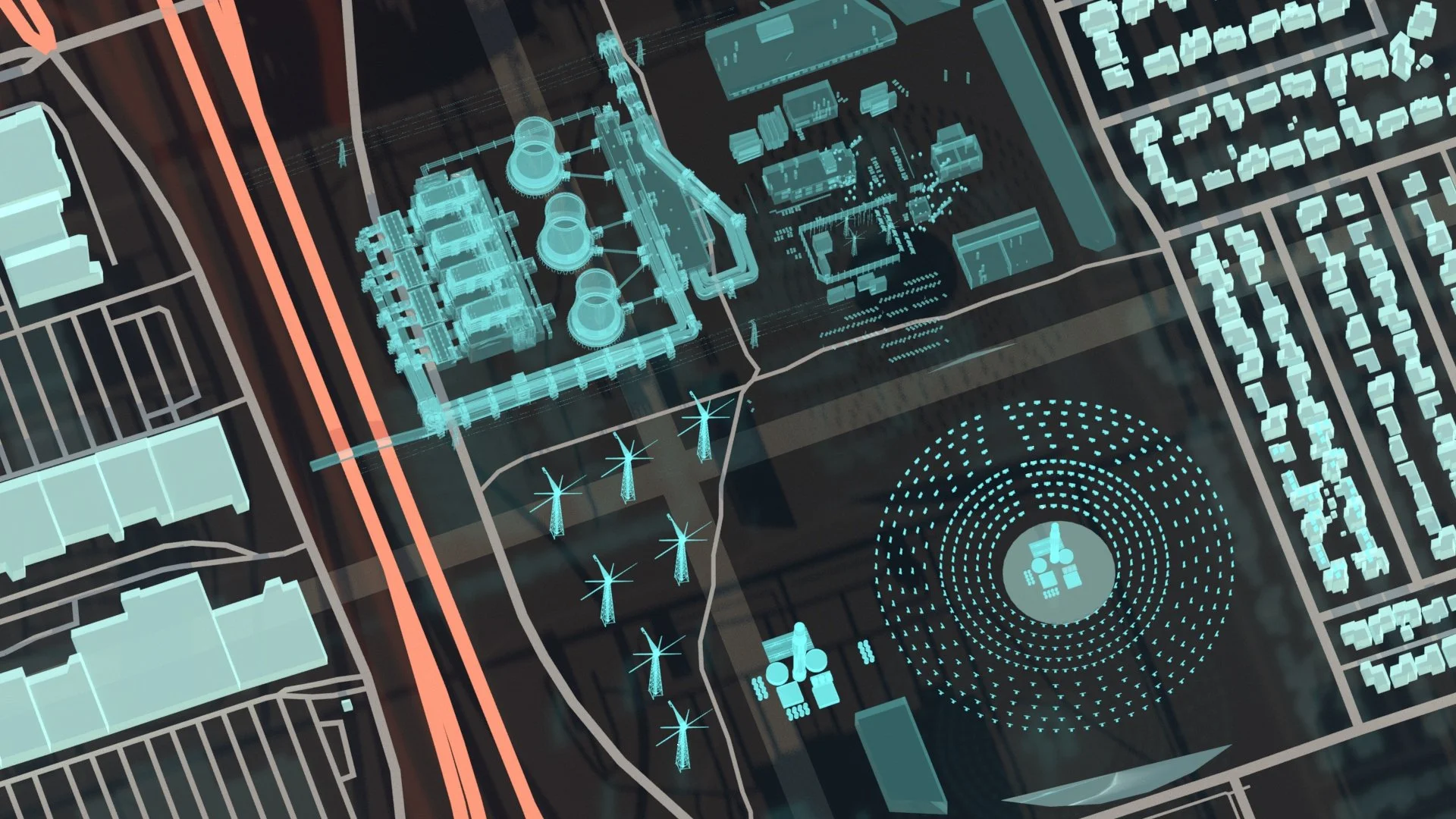
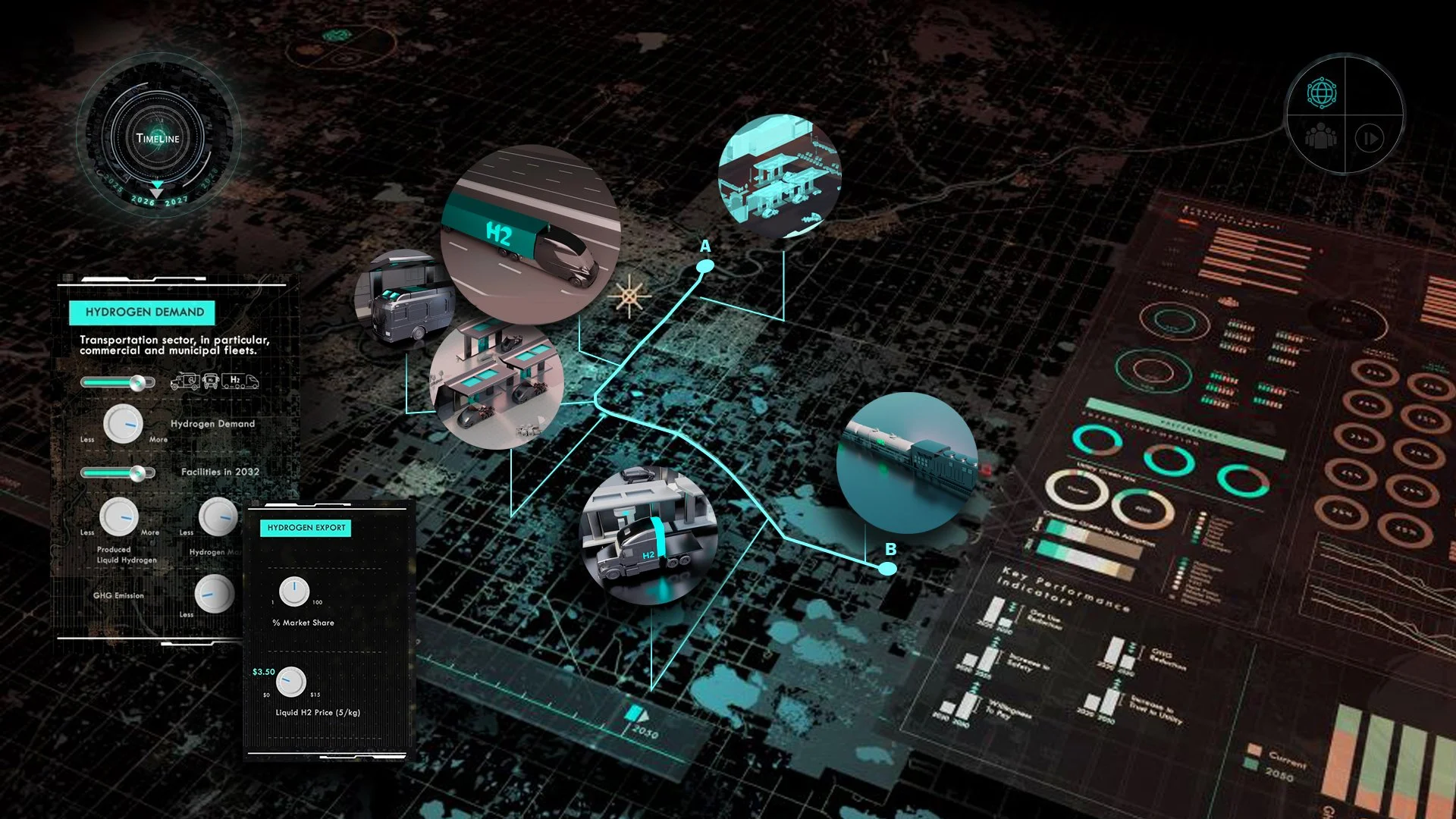
Transitioning to Hydrogen in Alberta
We supported the transition to a hydrogen economy by developing a Synthetic Twin set in the hydrogen-powered Alberta of 2030, creating a comprehensive, risk-informed framework to guide standardized provincial training and certification for the hydrogen workforce.
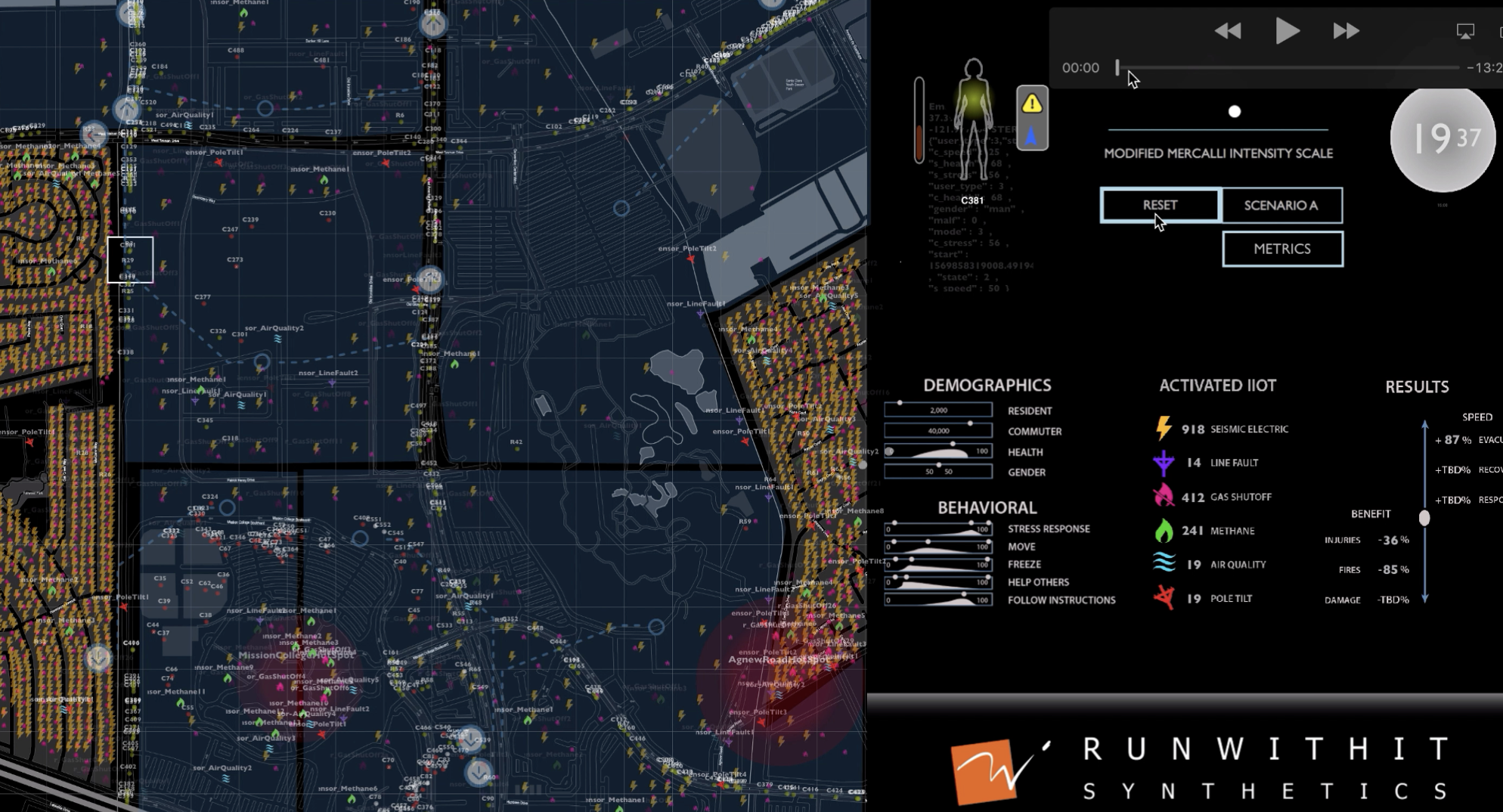
An IIoT Earthquake in Silicon Valley
Utility infrastructure data can guide emergency responders and improve AI-driven communications and evacuation through IIoT systems. To demonstrate this, RWI synthesized Silicon Valley’s utility networks and commuter population, then simulated a ‘synthetic earthquake’ to analyze human behavior, infrastructure impact, and emergency response in real-time.
Assessing Solar Risks from Space
Space-weather events from increased solar activity can unexpectedly disrupt the electrical grid, requiring cross-disciplinary approaches to assess risks to people and infrastructure. RWI launched its HoloDeck in 2022 to simulate space-weather impacts on a synthetic grid of the entire U.S. Northeast during a collaborative weather-to-power grid exercise with CHESS and the National Science Foundation.
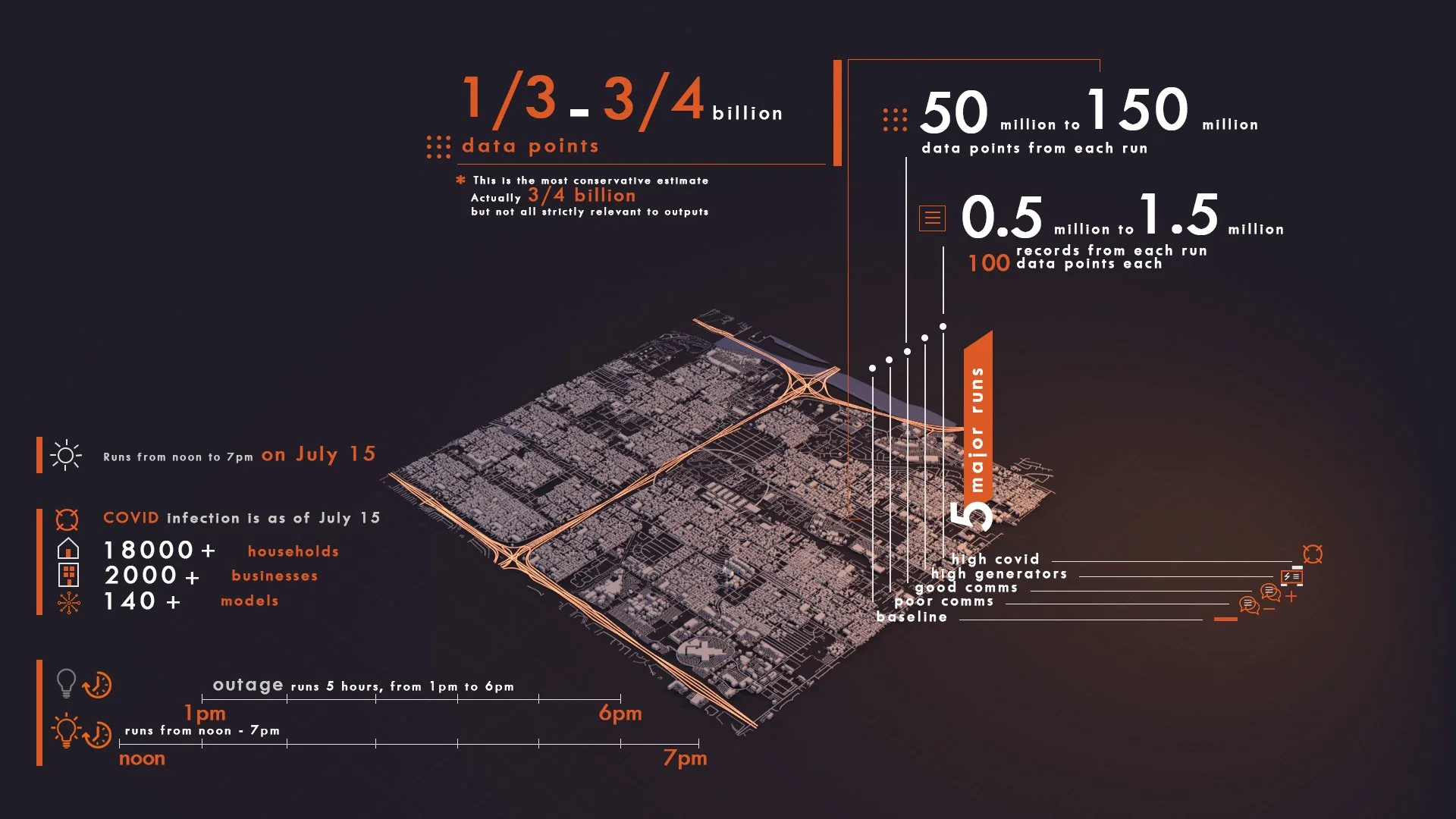
COVID Modelling
Cascading disasters combining medical events and infrastructure failures are difficult to plan for due to limited historical data and the complex interplay among risks and the health and well-being of vulnerable populations. Selected by EPRI’s Incubatenergy® Labs Challenge, RWI created a Synthetic Twin to model and assess resilience during a COVID-19 outbreak coupled with a grid outage.
Empowering the DOD’s Energy Transition
RWI and the Electric Power Research Institute partnered in the AFWERX Showcase to create a virtual twin sandbox for USAF Bases, enabling hyper-localized, data-driven decision-making to support the DOD’s energy transition, mission readiness, and resilience.