RWI Synthetic Twins bring municipalities to life in dynamic, human-centred simulations, integrating the built environment, alongside time, simulations, policy, and data, enabling municipalities, governments, and developers to simulate, visualize, and plan complex urban developments with high-fidelity estimates that always include the human factor.
We remove the guesswork and decrease decision-making time by 20% through our consensus-building, converged data platforms. This means faster scenario testing, improved project alignment, increased transparency, higher trust and engagement, and a higher ROI on capital investment, with 3rd-party estimates demonstrating up to $1.5 billion in savings over 10 years.
Synthetic Twins not only provide a vital cost-saving tool for efficiency but also secure better futures that prioritize people.
Connected Intelligence
Face complex social, investment, and policy challenges in your region with data-backed solutions activated by intelligent, 6D sandboxing.
Ensuring security and resiliency investments in critical services and utilities are quantified, comprehensive and prepared for the unprecedented.
Active Intelligence
Forecasting Electrification in Calgary
New grid load dynamics challenge traditional forecasting, prompting utilities like ENMAX Power to rethink existing processes. We addressed this by creating a 6D Synthetic Twin of Calgary that forecasts 2050 electrification demand with inflectable scenarios.
Youth Belonging
Youth sense of belonging is challenging to quantify, but it’s also a key indicator of a community’s connectedness and social health. Improved belonging can facilitate everything from classroom attendance in the present to increasing economic growth in the future. Planning and social services can utilize Synthetic Twins and Populations to test, forecast, and sandbox the various measures that can improve youth’s sense of belonging.
Establishing Social Infrastructure
There are few established tools for planning sustainable, resilient social infrastructure, despite communities increasingly requiring valuable, data-driven insights for long-term service strategies. RWI Synthetics addressed this by creating benchmarks from international best practices and running five future-focused sandbox scenarios for a client community.
High-Fidelity Infrastructure Forecasting
Amid housing crises and rapid population growth, RWI used Synthetic Twin intelligence to forecast, sandbox, and produce a high-fidelity estimate of the full annual infrastructure and service costs for a large municipal development at full build-out.
Disease Conditions and Connected Care
RWI is receiving advisory support and funding from NRC IRAP to research mapping disease conditions in rural and remote synthetic populations. This work, part of an international consortium under the Eureka ITEA cluster, models, analyzes, and visualizes the deployment of connected care interventions.
Accessible Mobility in Kuala Lumpur
Kuala Lumpur faces escalating pollution and greenhouse gas challenges due to population growth, traffic congestion, and reliance on private vehicles. As a finalist in the Toyota Mobility Foundation’s challenge, RWI’s Synthetic Kuala Lumpur modeled residents’ lives and city infrastructure to explore policies that improve inclusivity and accessibility through 2040.
Measuring Water Efficiency in California
Water efficiency is critical for thriving cities, supporting populations and industries while mitigating climate change and drought impacts, especially in regions like Southern California. We modeled residential water use by rethinking how usage behaviors are measured and integrating age, demographics, population, and time-of-day data.
Quantifying Intervention Impacts
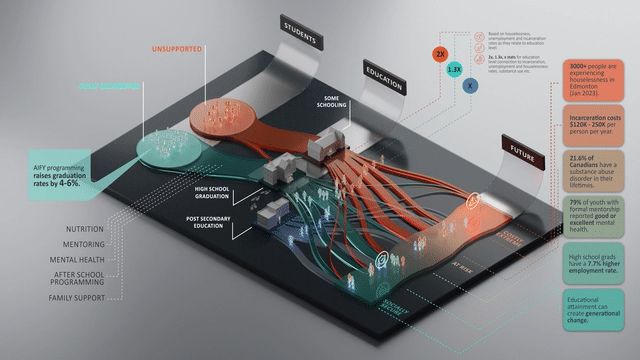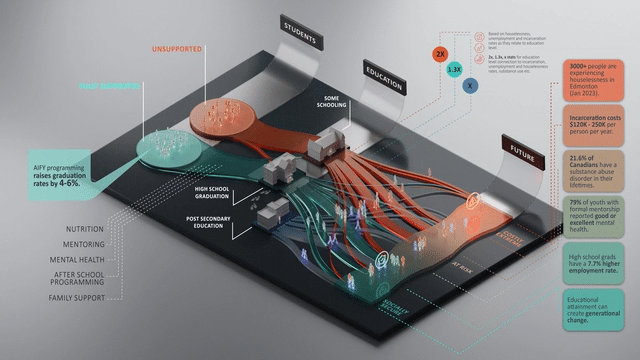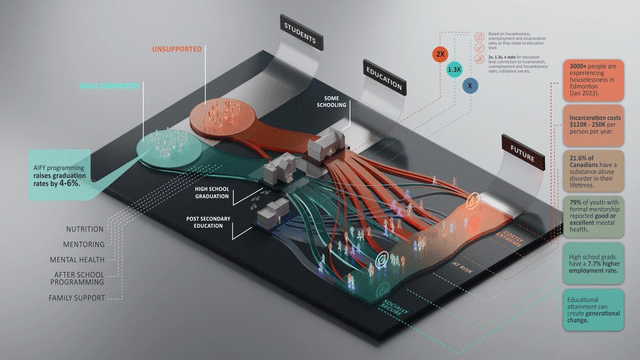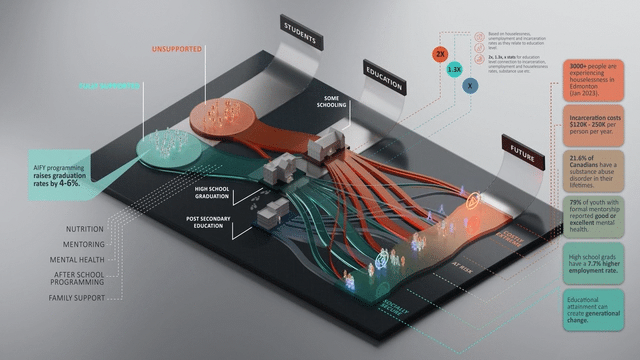
Communities have a timely opportunity to boost graduation rates and support at-risk youth through social infrastructure and programs, yet many organizations rely on anecdotal evidence to show impact. Our award-winning work with United Way Alberta Capital Region quantified the future impacts and ROI of their youth interventions.
Simulating Extreme Cold in Nashville
In a pilot with the Tennessee Valley Authority, we simulated an extreme cold snap and power outage in Nashville to show grid impacts and community vulnerabilities, particularly in lower-income neighborhoods.
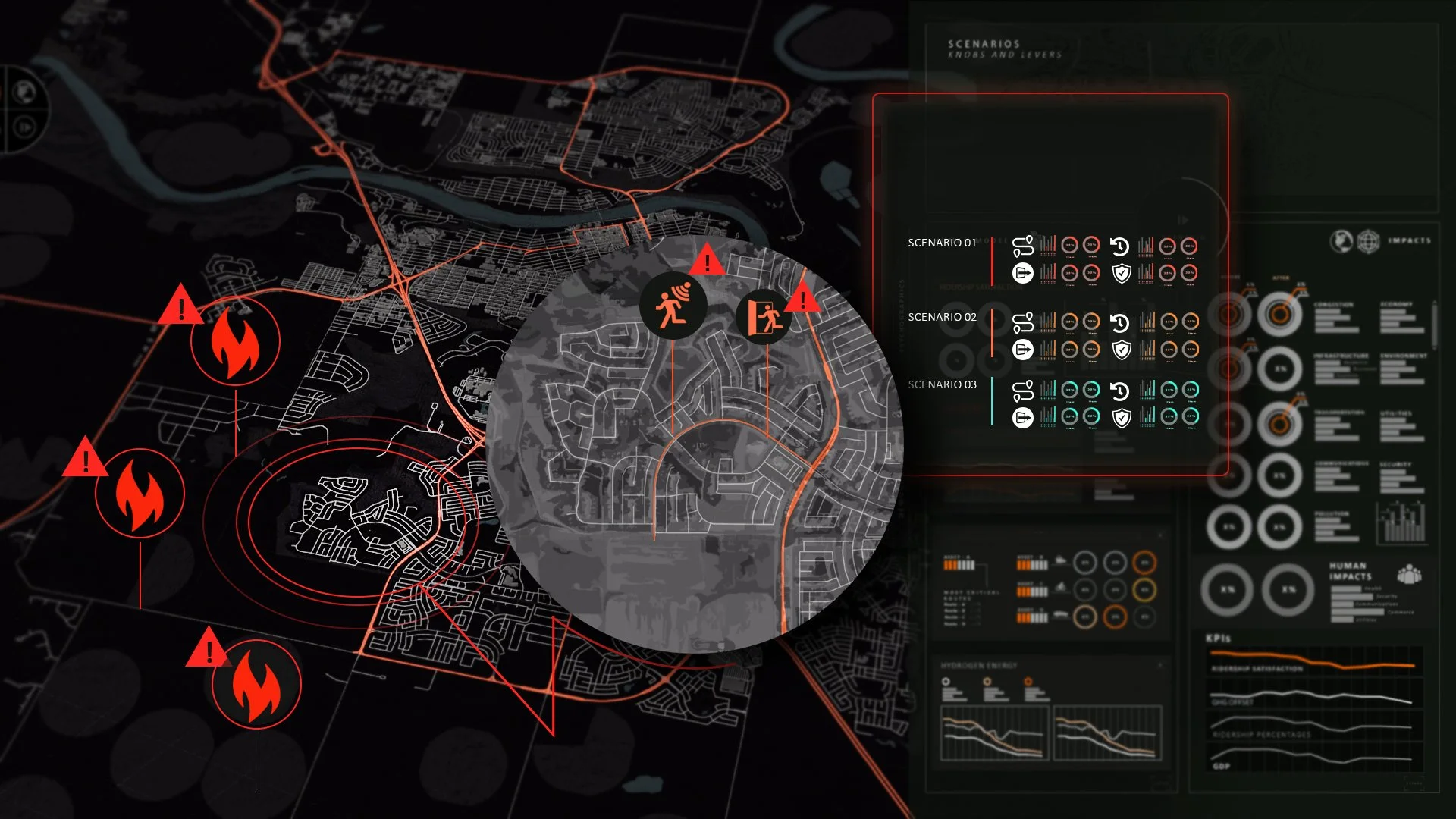
Synthesizing Wildfire Evacuations
In Western Canada, rising urban-wildfire interactions prompt emergency responders to identify infrastructure and policy risks, and RWI’s Synthetic Intelligence helps municipalities find the most efficient, cost-effective, and human-focused evacuation options.